Project Overview
This audio programming project demonstrates the implementation of dynamic, immersive audio systems using FMOD Studio integrated with Unreal Engine 5.2. Inspired by AAA titles like Ghost of Tsushima and Red Dead Redemption 2, the project focuses on creating responsive audio that enhances player immersion through surface-based footsteps, spatial ambience, and environmental reverb. The artefact showcases a third-person character with dynamic footstep sounds that change based on three different surface types (grass, wood, concrete), complemented by adaptive ambient soundscapes including spatially-aware bird chirping and interior room reverb with atmospheric lighting hum.
Development Time: 1 months
Team Size: Solo project
Role: Audio Programmer & Sound Designer
Platform: PC
Screenshots




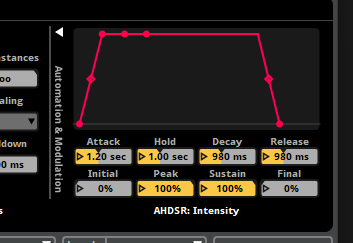
Technical Focus
This project explores the complexities of audio programming in interactive environments, examining:
- Middleware Integration: Manual FMOD Studio integration with Unreal Engine 5.2
- Dynamic Audio Systems: Surface-detection and parameter-driven sound switching
- Spatial Audio: 3D positioned ambient cues with distance attenuation
- Adaptive Soundscapes: Context-aware reverb and environmental audio transitions
- Animation Synchronization: Precise footstep timing using animation notifications
Key Features
🎵 Dynamic Footstep System
-
Multi-Surface Detection: Three distinct surface types with unique audio characteristics
- Grass: Soft, muffled steps with natural vegetation sounds
- Wood: Crisp, hollow footsteps with slight resonance
- Concrete: Solid, clear impact sounds for paved surfaces
- Procedural Variation: Randomized pitch and volume for each footstep to prevent repetition
- Animation Sync: Perfectly timed footstep sounds using Unreal Engine animation notifies
- 3-Band EQ Processing: Dynamic frequency adjustments for different materials
🌳 Adaptive Ambient Soundscape
- Exterior Ambience: Spatially-positioned bird chirping with distance-based attenuation
- Scattered Audio Placement: Multiple bird sounds distributed naturally across the environment
- Interior/Exterior Blending: External sounds audibly muffled when entering enclosed spaces
- Proximity-Based Volume: Dynamic sound levels as player approaches or leaves ambient sources
🏛️ Environmental Reverb System
- Large Room Simulation: Natural reverberation effect for enclosed spaces
- Snapshot-Based Transitions: Smooth reverb activation when entering interior spaces
- Contextual Footsteps: Modified footstep sounds reflecting room acoustics
- Interior Ambience: Atmospheric lightbulb buzz/hum adding to environmental presence
- Wall Occlusion: External sounds properly muffled through walls
Technical Implementation
FMOD Studio Architecture
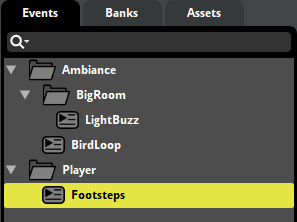
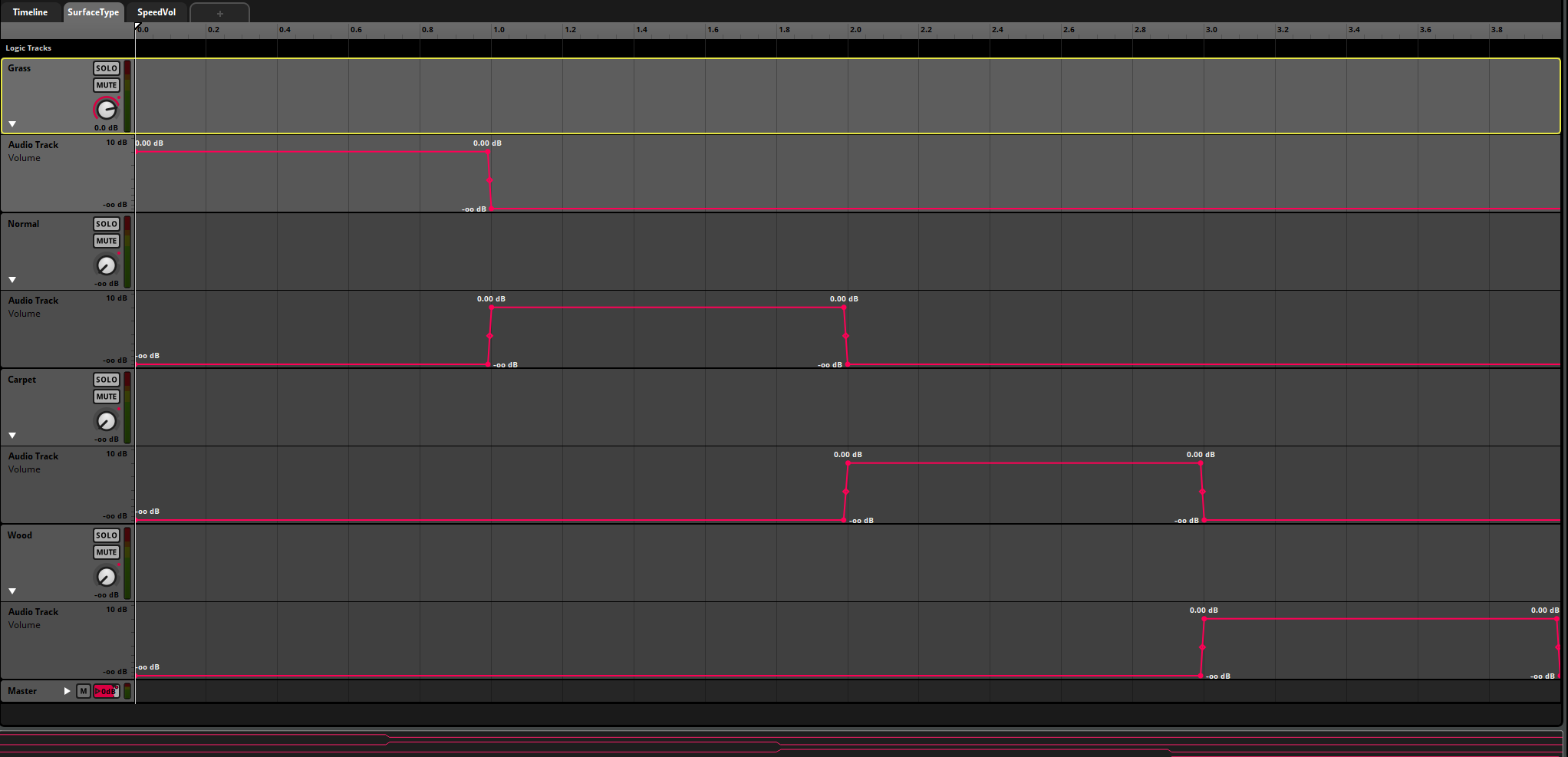
Footsteps Event System
The footstep system uses a parameter-driven approach with automatic surface detection:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Event: Player/Footsteps
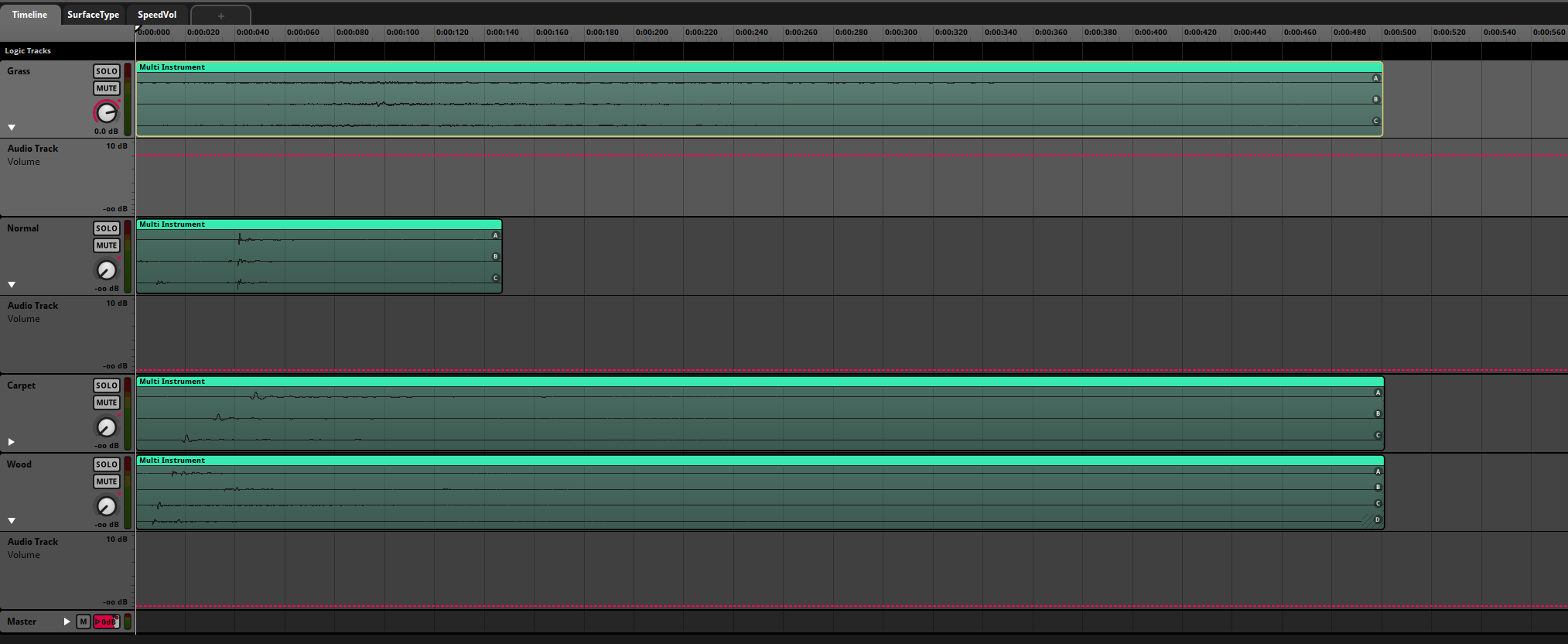
├── Timeline (4 Audio Tracks)
│ ├── Grass (3 variations)
│ ├── Wood (3 variations)
│ ├── Concrete (3 variations)
│ └── Default (3 variations)
├── Parameter: SurfaceType (0-3)
└── Effects Chain
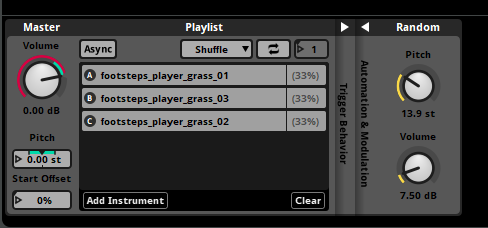
├── Random (Pitch: ±5%, Volume: ±3dB)
├── 3-Band EQ (per-surface)
└── Volume Automation
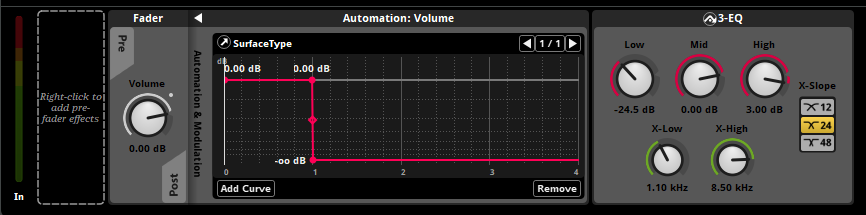
Parameter Automation Logic
- SurfaceType = 0: Grass sounds at 0dB, others muted
- SurfaceType = 1: Wood sounds at 0dB, others muted
- SurfaceType = 2: Concrete sounds at 0dB, others muted
- SurfaceType = 3: Default sounds at 0dB, others muted
Each surface track includes three variations to prevent audio repetition, with randomized pitch (±5%) and volume (±3dB) for natural variation.
Ambient Audio Configuration
Birds Chirping (Exterior)
Figure 1: Birds Chirping Ambience Cue
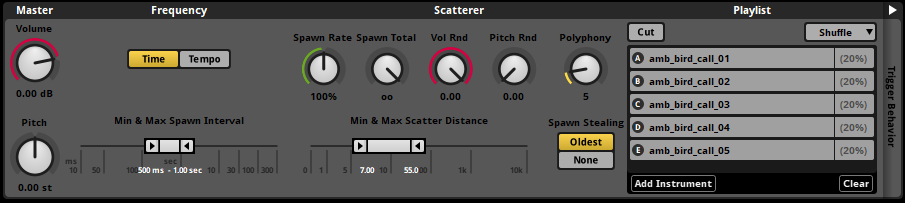
Figure 2: Settings for the Birds Chirping
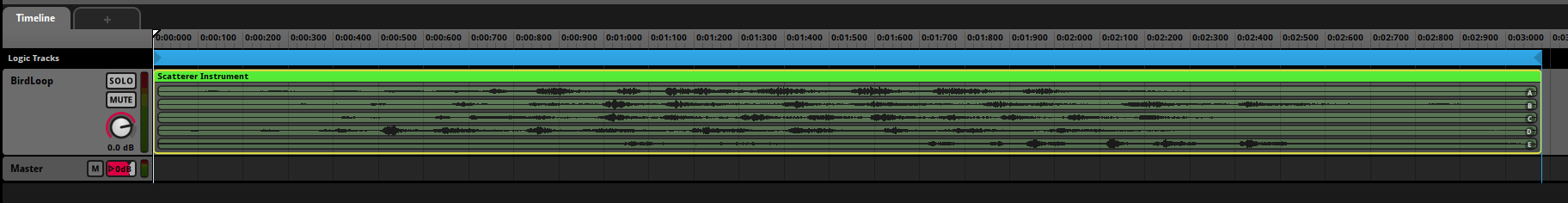
Figure 3: Birds Chirping sounds
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Event: Ambience/BirdsChirping
├── Scattered Instrument (5 bird variations)
├── Spawn Interval: 2-5 seconds
├── Scatter Distance: 15m radius
└── Effects
├── Random Pitch (±10%)
└── Random Volume (±5dB)
Interior Ambience
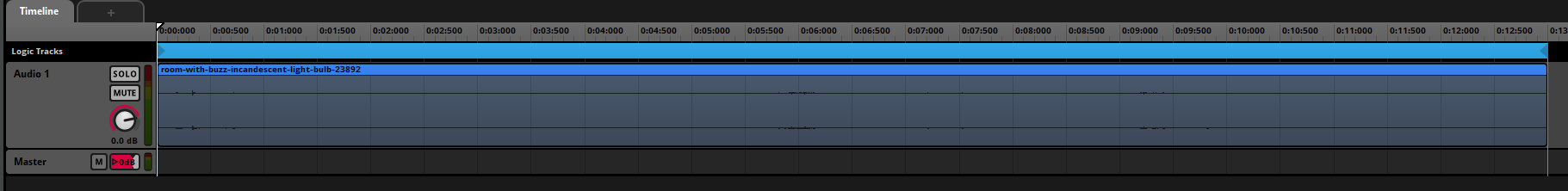
Figure 4: Lightbulb buzz/hum track
1
2
3
4
Event: Ambience/LightbulbHum
├── Looping Audio Track
├── Mixer Group: AmbienceInt
└── Snapshot-Controlled Reverb
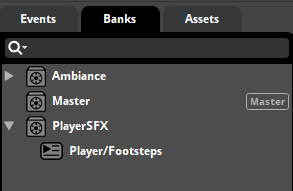
Mixer Architecture & Snapshots
The FMOD mixer uses grouped routing for precise control:
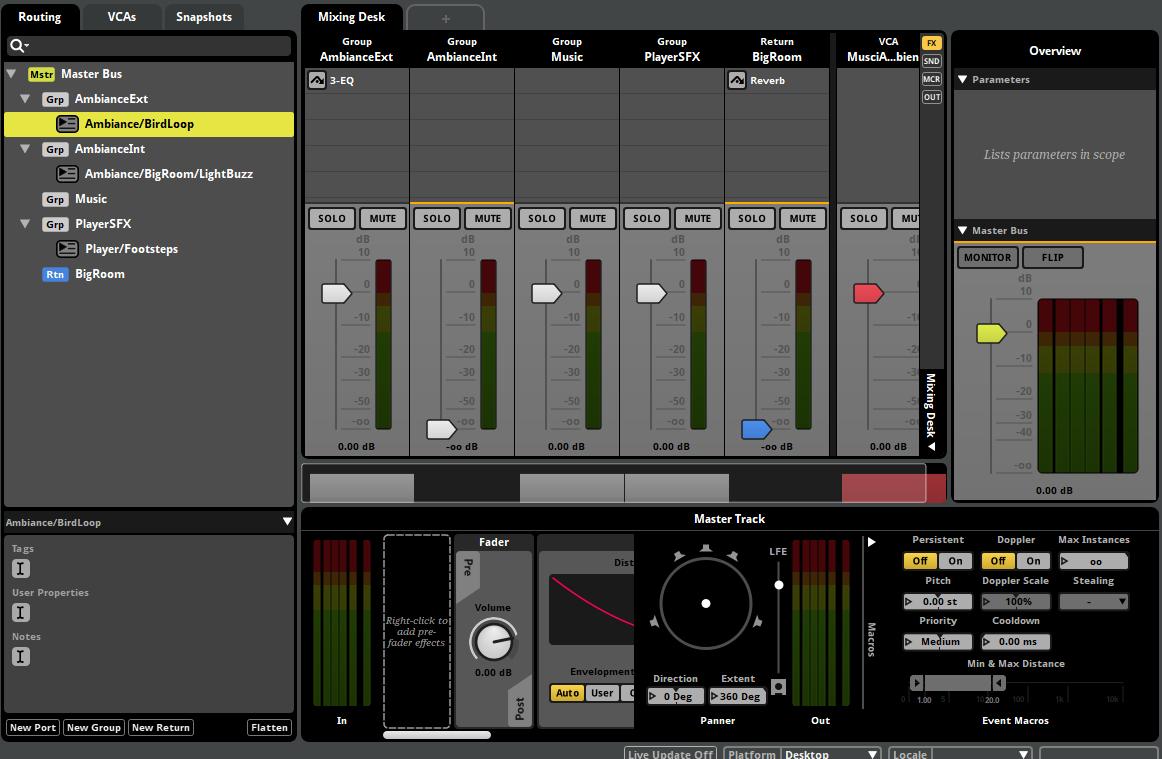
Figure 5: Mixer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Master Bus
├── AmbienceExt (External Sounds)
│ └── Birds Chirping
├── AmbienceInt (Internal Sounds)
│ └── Lightbulb Hum
├── PlayerSFX (Character Sounds)
│ └── Footsteps
└── Return: BigRoom (Reverb)
├── Attack: 0.5s
└── Release: 1.0s
Snapshot: BigRoom Interior
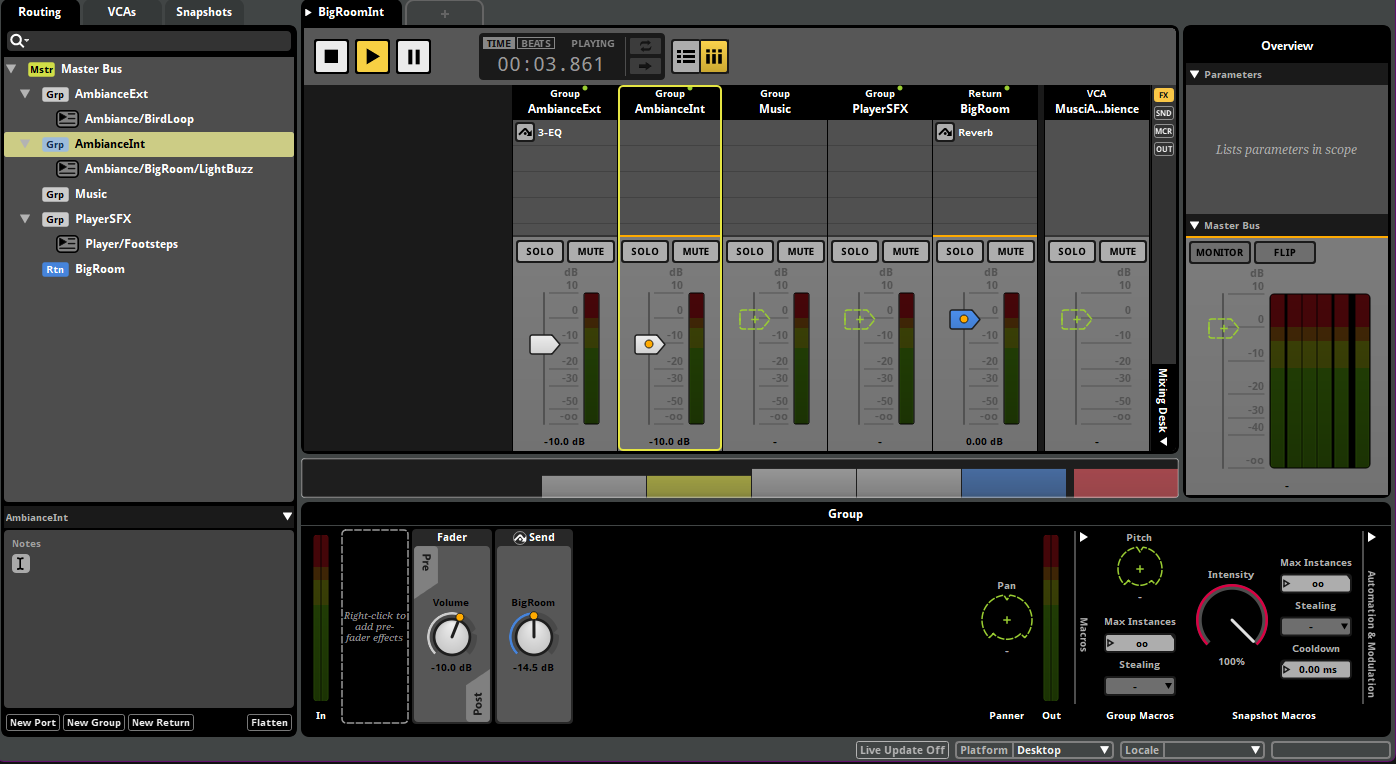
Figure 6: Snapshot of AmbienceInt
- Activates reverb return bus
- Attenuates external ambience by -6dB
- Applies low-pass filter to external sounds (simulating wall occlusion)
- Smooth 500ms transition in/out
Unreal Engine 5 Integration
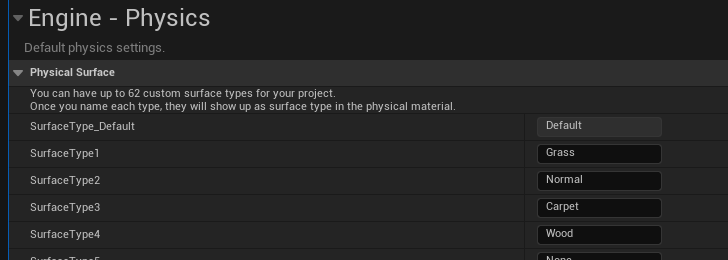
Physical Surface Setup
1
2
3
4
5
// Project Settings > Physics > Physical Surfaces
PM_Grass (SurfaceType1) = 0
PM_Wood (SurfaceType2) = 1
PM_Concrete (SurfaceType3) = 2
PM_Default (Default) = 3
Animation Blueprint Logic
Character footsteps triggered via animation notifies:
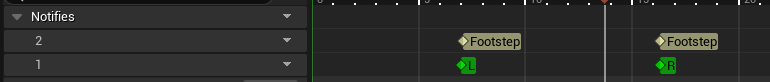
Figure 7: Footsteps notifies
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Animation: ThirdPersonRun
├── Notify: LeftFoot (Frame 15)
│ └── Play FMOD Event 2D (Player/Footsteps)
│ └── Set Parameter: SurfaceType (from trace hit)
└── Notify: RightFoot (Frame 45)
└── Play FMOD Event 2D (Player/Footsteps)
└── Set Parameter: SurfaceType (from trace hit)
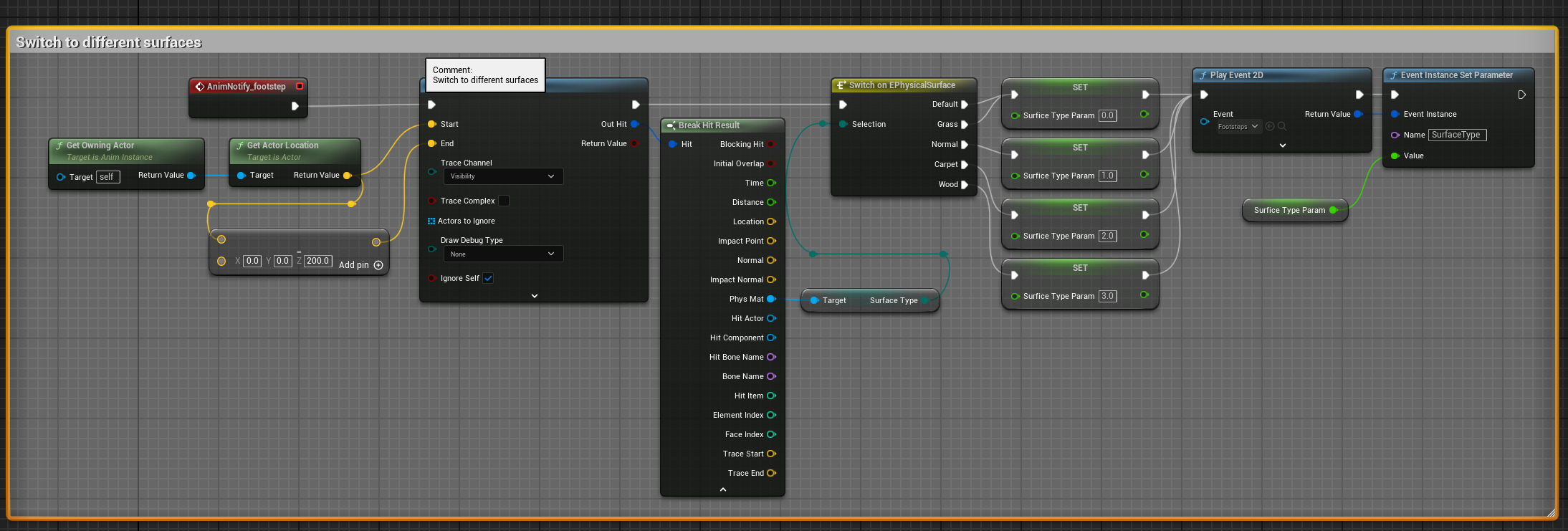
Figure 8: Character Animation Blueprint
Surface Detection System
- Line trace from character foot to ground
- Query physical material of hit surface
- Convert material to SurfaceType parameter value
- Pass parameter to FMOD event before playback
Spatial Audio Placement
Ambient cues placed as 3D FMOD Audio components:
- Birds Chirping: Positioned near grass area with 30m max distance
- Lightbulb Hum: Inside big room, 15m max distance
- Snapshot Trigger: Box collision volume activating BigRoom snapshot
Technical Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1
Manual FMOD Integration with UE5.2
Problem: No official marketplace plugin available for Unreal Engine 5.2 Solution: Manually integrated FMOD by:
- Downloaded FMOD Studio and Unreal Engine integration files
- Created Plugins folder in project directory
- Extracted FMOD plugin files into Plugins/FMODStudio
- Regenerated Visual Studio project files
- Compiled plugin from source
- Created new FMOD Studio project and linked to Unreal project via settings
- Built initial bank structure and validated integration
Learning: Understanding plugin architecture and manual integration process deepened knowledge of Unreal Engine’s plugin system
Challenge 2
Animation-Footstep Synchronization
Problem: Footstep sounds playing inconsistently or out of sync with character animations
Solution:
- Created dedicated notify track in animation sequence
- Placed notifies precisely at foot-contact frames
- Added separate “L” and “R” notifies for complete animation montage
- Tested sync across different animation speeds
- Fine-tuned notify positions through iterative playtesting
Result: Perfect synchronization between visual footstep and audio playback at all animation speeds
Challenge 3
Interior Reverb Bleed
Problem: Reverb effect persisting for 2-3 seconds after leaving the big room
Solution:
- Adjusted snapshot Attack time to 500ms (entering room)
- Set Release time to 1000ms (leaving room)
- Optimized reverb tail length in effect chain
- Reduced pre-delay to minimize latency
Result: Reverb now dissipates within 1 second of leaving interior space, providing responsive environmental transition
Challenge 3
External Audio Occlusion
Problem: Bird sounds too prominent inside the big room, breaking immersion
Solution:
- Routed external ambience through dedicated mixer group
- Created snapshot that attenuates AmbienceExt by -6dB
- Applied low-pass filter (cutoff: 2kHz) when snapshot active
- Maintained spatial 3D positioning for realistic directionality
Result: External sounds appropriately muffled when inside, while maintaining spatial awareness of their location
Audio Design Philosophy
Inspiration from AAA Games
Ghost of Tsushima - Primary inspiration for footstep variety and environmental ambience placement. The seamless integration of natural sounds with character movement heavily influenced this project’s approach.
Red Dead Redemption 2 - Studied for comprehensive ambient soundscape design and how environmental audio responds to player location.
Subnautica - Referenced for underwater audio manipulation techniques, adapted here for interior/exterior transitions.
No Man’s Sky - Examined for dynamic surface-based audio and cockpit ambience design principles.
Design Principles Applied
Seamless Transitions: Surface changes detected instantly with no audio pops or gaps
Natural Variation: Randomization prevents audio fatigue while maintaining authenticity
Spatial Awareness: 3D audio positioning helps players understand their environment
Contextual Adaptation: Audio responds appropriately to player’s location and actions
Performance Optimization: Efficient event streaming and memory management for real-time audio
System Architecture Benefits
For Designers
- No-Code Audio Editing: All audio parameters adjustable in FMOD Studio
- Visual Event Creation: Timeline-based interface for complex audio behaviors
- Live Tuning: Real-time parameter adjustments while game is running
- Clear Organization: Logical event/bank structure for easy navigation
For Programmers
- Clean Integration: Well-defined interface between FMOD and Unreal
- Parameter-Driven: Single event handles multiple variations via parameters
- Memory Efficient: Streaming system loads only necessary audio
- Scalable Architecture: Easy to add new surfaces or ambient cues
For Players
- Enhanced Immersion: Responsive audio that reflects their actions
- Environmental Awareness: Audio cues provide gameplay information
- Natural Soundscape: Varied, realistic audio prevents monotony
- Smooth Experience: No jarring transitions or audio glitches
Learning Outcomes
Technical Skills Developed
Audio Middleware Mastery: Deep understanding of FMOD Studio’s event system, mixer architecture, and parameter automation
Integration Expertise: Manual plugin integration, understanding build systems and engine architecture
Spatial Audio: 3D positioning, distance attenuation, occlusion simulation, and reverb zones
Performance Optimization: Audio streaming, memory management, and event instantiation best practices
Signal Processing: Applied EQ, compression, reverb, and randomization for realistic audio
Game Development Insights
Audio Programming Workflow: Understanding the complete pipeline from sound design to in-game implementation
Cross-Discipline Communication: Learning to think from both programmer and sound designer perspectives
Iteration Importance: Multiple testing cycles crucial for achieving natural-feeling audio
Documentation Value: Clear technical documentation essential for complex audio systems
Scope Management: Balancing ambition with timeline constraints and technical limitations
Future Enhancements
If expanding this project, I would implement:
Dynamic Music System
- Adaptive music that responds to player actions
- Vertical layering based on intensity/danger
- Smooth transitions between exploration and combat themes
Advanced Occlusion
- Real-time raycast-based audio occlusion
- Material-based filtering (wood walls vs concrete walls)
- Doorway audio propagation
Reflection
Developing this audio system was an invaluable learning experience that opened my eyes to a department I had previously overlooked during my academic career. Working with FMOD Studio changed my perspective on how game audio is designed and implemented. The most significant challenge was understanding the complete pipeline from sound design to implementation. Initially approaching from a programmer’s perspective, I had to adapt to think like an audio designer, considering factors like frequency balance, spatial positioning, and player psychology. The manual FMOD integration taught me valuable lessons about engine architecture and plugin systems. While frustrating initially, this challenge forced me to understand the low-level connection between middleware and game engines. Synchronizing footsteps with animations revealed the importance of precise timing in creating believable character audio. The solution required iteration and careful attention to frame-by-frame animation playback. The reverb bleed issue taught me about signal processing and the importance of attack/release timing. Understanding how audio effects behave over time was crucial to creating smooth environmental transitions. Overall, I’m satisfied with the results achieved within the project timeline. The artefact successfully demonstrates core audio programming concepts while providing an immersive player experience. While not matching AAA production quality, it effectively showcases the fundamental techniques used in modern game audio. This project significantly improved my technical abilities and gave me deeper appreciation for sound designers’ craft. The skills learned will be invaluable in future game development projects requiring audio implementation.
Academic Context
Institution: Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge
Course: BSc Computer Games Technology
Module: MOD008619 - Technical Development for Games
Element: 010 - Audio Programming
Academic Year: 2023/24
Grade: B
Links
-
Download the full academic research
This project demonstrates my ability to integrate professional audio middleware with Unreal Engine, implement dynamic audio systems, and create immersive soundscapes that enhance player experience. It showcases both technical programming skills and understanding of audio design principles.
